Are you the one who is curious about this emerging technology that is going to radically improve banking, supply chain, and other transaction networks and going to create new opportunities for innovation? Well, you are just at the right place… : – )
As we know, Businesses contain many examples of networks of individuals and organizations that collaborate to create value and wealth. These networks work together in markets that exchange assets in the form of goods and services between the participants.
So! within all this, What Blockchain Actually Do???
Well, Blockchain provides the basis for a dynamic shared ledger that can be applied to save time when recording transactions between parties, remove costs associated with intermediaries and reduce risks of fraud and tampering.
Hopefully, from above video, your brain might be also clear about how actually Blockchain Work… : – )
For, how the Block within Blockchain works? Let’s see another interesting video;
So! What is the Need of Blockchain?
In today’s world, Business Networks are getting benefit from connectivity. In which participants are customers, suppliers, banks and partners and objective is Cross geography & regulatory boundary. The Wealth is generated by the flow of goods & services across the business network in transactions and contracts. And Markets are central to this process, like Public (fruit market, car auction), or Private (supply chain financing, bonds).
So, during this, when we deal with “Transferring Assets” and building values that includes anything that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value, is an asset.
That includes two types of assets;
- Tangible, E.g. a House, Cash (Has property of anonymity)
- Intangible, The Intangible assets subdivide;
- Financial, e.g. bond
- Intellectual, e.g. patents
- Digital, e.g. music
So to take the record of “Transferring Assets”, we have Ledgers…
Ledger is THE system of record for a business.
Most if not all business operate on public or private networks. Tangible and intangible assets must be transferred across networks to network participants. Ledgers are used to document all those transactions, and networks are governed by a contract. At the highest level, a blockchain is a trusted, distributed ledger with shared business processes.
Business will have multiple ledgers for multiple business networks in which they participate.
That actually care for following two things;
- Transaction–an asset transfer onto or off the ledger
- E.g. Sajid gives a car to Bilal (simple).
- Contract–conditions for transaction to occur
- E.g. If Bilal pays Sajid money, then car passes from Sajid to Bilal (simple)
- E.g. If the car won’t start, funds do not pass to Sajid (as decided by the third-party arbitrator) (more complex)…
So here we are introducing the concept of Blockchain… A Trusted Distributed Ledger…
Talking about the challenges of current business networks: multiple manual ledgers. This means that all participants in a network must update or audit their own ledgers, which is inefficient, error-prone, and insecure…
Following is the clear picture of inefficient, expensive, vulnerable;
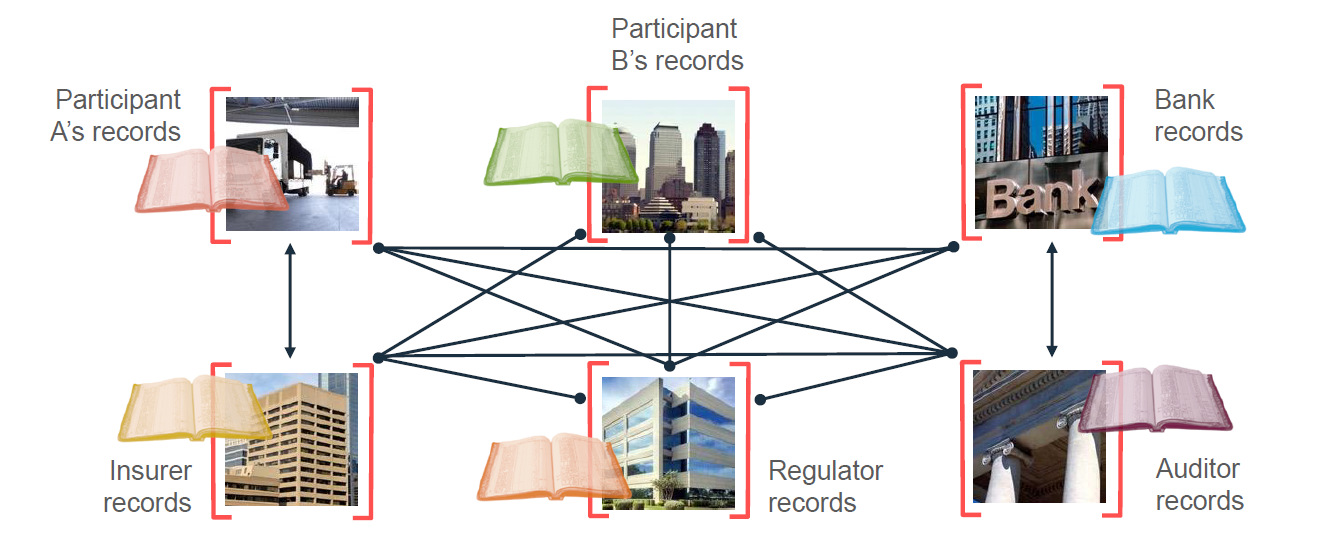
So, with Blockchain, a shared replicated and permission ledger build with consensus, provenance, immutability and finality…
Following is the clear picture of it;
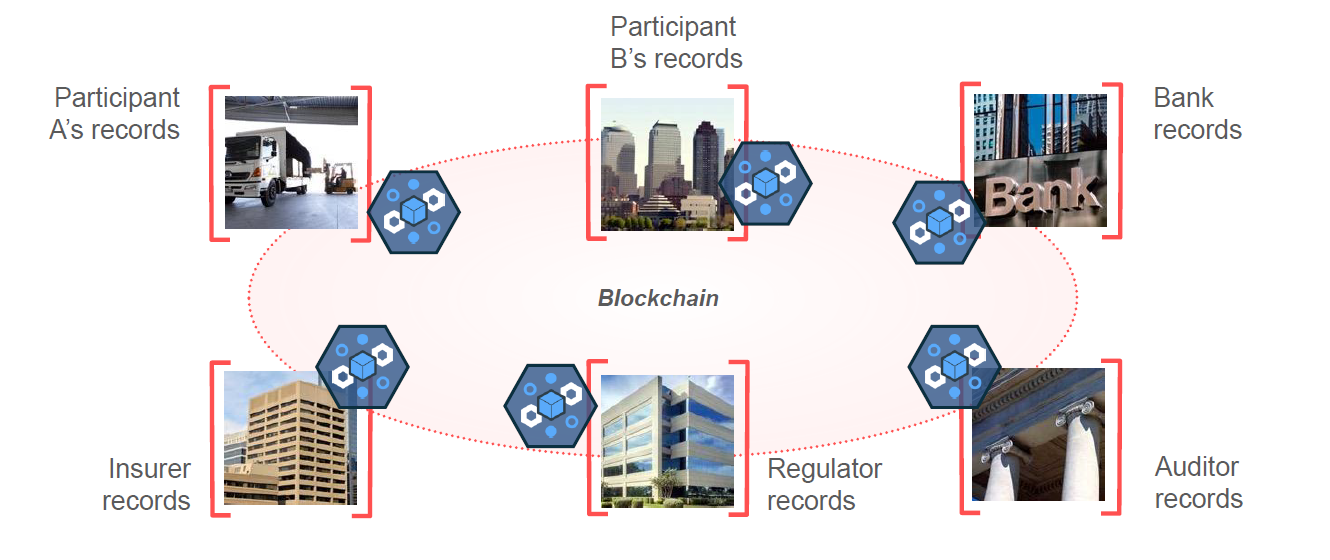
So, here we can use the term, Blockchain for Business;
What is Blockchain for Business?
It’s the combination of a shared, unalterable ledger and smart contracts that streamline business processes and open new opportunities for innovation. The consensus among blockchain network members eliminates costly risks and inefficiencies as assets change hands throughout a business network.
i) Shared Ledger;
Records all transactions across the business network.
- Shared among participants.
- Participants have own copy through replication
- Permissioned, so participants see only appropriate transactions
- THE shared system of record
ii) Smart Contract;
Business rules implied by the contract … embedded in the Blockchain and executed with the transaction
- Verifiable, signed
- Encoded in programming language
- Example:
- Defines contractual conditions under which corporate Bond transfer occurs.
iii) Privacy;
The ledger is shared, but participants require privacy.
- Participants need:
- Appropriate confidentiality between subsets of participants
- Identity not linked to a transaction
- Transactions need to be authenticated
- Cryptography central to these processes
iv) Trust;
The ledger is a trusted source of information.
- Participants endorse transactions
- Business network decides who will endorse transactions
- Endorsed transactions are added to the ledger with appropriate confidentiality
- Assets have a verifiable audit trail
- Transactions cannot be modified, inserted or deleted
- Achieved through consensus, provenance, immutability and finality.
Now, at this point, a question arises, Why is Blockchain relevant for our Business?
Well, there are lot of benefits through which blockchain can add true value;
- Saves time: Transaction time from days to near instantaneous.
- Removes cost: Overheads and cost intermediaries.
- Reduces risk: Tampering, fraud & cybercrime.
- Increases trust: Through shared processes and recordkeeping.
For example, for financial services network, a business network that runs on a blockchain can speed up transaction processes and audits. That in turn reduces costs and can lead to greater customer satisfaction. A business that runs a supply chain network can benefit from blockchain by reducing errors in shipments, have better tracking or materials, and reduce the risk of illicit tampering of records.
Need to remember that blockchain is still an emerging technology. One suggestion for those looking to adopt blockchain is to start with a simple first use case. Business owners need to start small and then look for more ways to grow and expand the use of blockchain networks. Speaker briefly mentions some of the roles in a business such as regulators, market makers, and industry groups.
By talking about Blockchain, we must have mentioned IBM here. IBM plays a major role for Blockchain. It was an IBM project which IBM outsource for accessibility of people.
IBM is involved in blockchain for business development. IBM is a premier member of the Linux Foundation Hyperledger Project. IBM also has other services and technologies to help you build a blockchain network such as IBM Cloud (IBM Cloud) and Docker containers. IBM provides support and engagement to help you build with blockchain.
- Hyperledger, a Linux Foundation Project:

It is a collaborative effort created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies for business, Announced December 2015, now over 140 members, Open source, open standards, open governance. One active framework (“Fabric”) and seven projects in incubation. IBM is a premier member of Hyperledger.
- Hyperledger Composer: Accelerating time to value;
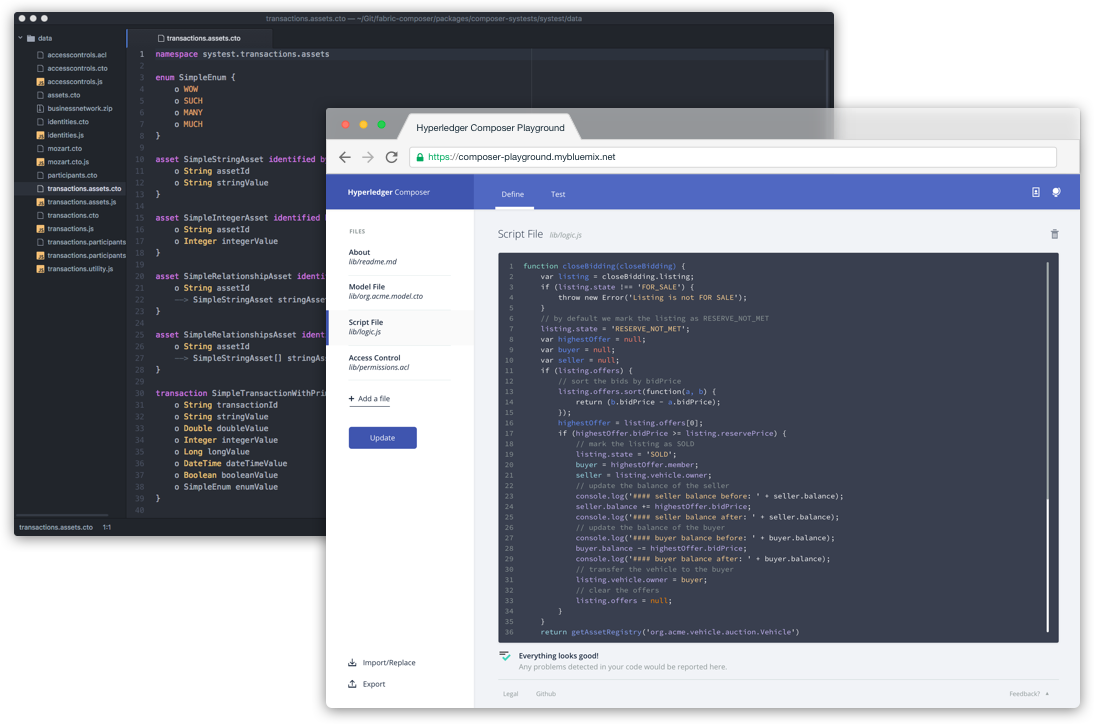
It helps you accelerate time to value because you no longer need to Render smart contracts in chaincode.
It is a suite of high-level application abstractions for business networks. Emphasis on business-centric vocabulary for quick solution creation, Reduce risk and increase understanding and flexibility.
IBM is a premier member of Hyperledger.
Hyperledger Composer is a faster, easier way to build networks rather than build with chaincode in the Go programming language.

Features;
- Model your business networks, test and expose via APIs
- Applications invoke APIs transactions to interact with business network
- Integrate existing systems of record using loopback/REST
- Fully open and one of eight Hyperledger projects
Transfer assets in a business blockchain
Transferring assets is the heart of blockchain. How can people buy and sell or transfer goods in a business network without any central governing body or policy?
The following video demonstrates exactly that: how an asset, such as a car, can be transferred (bought or sold) to other people. That process is compared to the traditional way assets (goods or services) are transferred between different people.
LIVE DEMO!
So, hope you have got a good JumpStart with Blockchain… For a detailed Hands-on with Blockchain, see the blog post here;





