Motivation
Well, if you’re looking to improve your business processes to provide a systematic approach. Or seeking ways to improve your organization to increase productivity, low cost and increase revenue by comprehensive change management of business processes then IBM BPM (Business Process Manager) is the tool for you.
What is IBM Business Process Manager?
It is a comprehensive Bussiness Process Manager Platform. It provides a strong set of tools to “Authorize“, “Test” and “Deploy” business processes.
- There are following two simplified editions of the product to support various levels of complexity and involvement with business process management;
- IBM BPM Express;
- For a small number of users – single server, no clustering. Low entry price. Install in a few clicks
- IBM BPM Server;
- For multi-project improvement programs, with high business involvement; Basic system integration support.
- Rapid time-to-value: improved user productivity.
- Extended support for high-volume process automation, with high quality-of-service.
- Built-in SOA components for extensive enterprise-wide service integration, orchestration
- IBM BPM Express;
If we particularly talk about IBM BPM Server;
- It provides full visibility and insight to managing those business processes.
- It provides tooling and runtime for process design, execution, monitoring, and optimization, along with basic system integration support.
- It’s ideal for multi-project improvement programs that focus on workflow and productivity, scaling easily from initial project to enterprise-wide programs.
BPM is a business-led solution, and any toolset that is used to implement it must support that involvement.
BPM Vision
“BPM is the means by which companies and governments improve their operations by using internal business expertise in new, scalable ways. Improvement is achieved by directly engaging business people in the design, definition, and creation of enterprise-class process applications.”
What Does a Business Process Manager Do?
In general, a business process manager evaluates, designs, executes, measures, monitors and controls business processes. Managers work to ensure that business process outcomes are in harmony with an organization’s strategic goals.
It helps to prioritize your work, but still gives you the visibility and control needed to ensure operations are running smoothly.
- When a process needs to change, you can quickly implement the necessary changes and put them into action immediately.
Three Themes
We can also describe BPM with three common themes;
- Goal;
- The BPM goal is efficient and effective business processes with visibility.
- All companies have processes. Perhaps the visibility of processes can be varied.
- BPM is a way to increase that visibility and hence give direction to the continued efficiency of the processes.
- All companies have processes. Perhaps the visibility of processes can be varied.
- The BPM goal is efficient and effective business processes with visibility.
- System;
- The BPM system is the management of people-to-people work steps, system-to-system communications, or person-to-system interactions.
- In true BPM, all aspects of a system are important, including human interactions. True BPM seeks to define and visualize all aspects of your process regardless of what role or system is conducting that part of the work.
- The BPM system is the management of people-to-people work steps, system-to-system communications, or person-to-system interactions.
- Results;
- The BPM expected result is process improvement that brings about financial benefits and customer and employee satisfaction.
- Provides many beneficial outcomes to the client.
- The BPM expected result is process improvement that brings about financial benefits and customer and employee satisfaction.
BPM Lifecycle
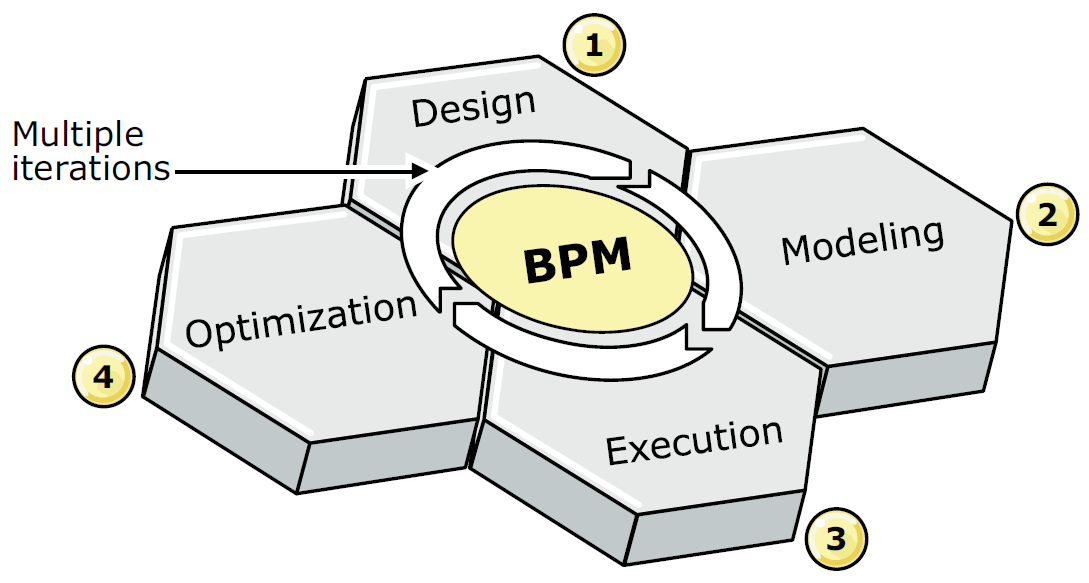
In BPM lifecycle we have four phases;
- Design
- Modeling
- Execution
- Optimization
By using BPM lifecycle, its become clear that there are opportunities to use the expertise of business and IT to collaborate in each phase of the lifecycle.
Using this approach to BPM, the business process is stable and on target. This stability is because of the overall iterative improvement cycles in keeping up with business goals, business change, and opportunities within each phase to make critical adjustments.
- Business and IT working in concert throughout the BPM lifecycle require a clear set of goals for each phase.
- Matched against those lifecycle phase goals are the responsibilities for each group.
- Clearly, the governance of the business process varies at each phase for each group, but the involvement of both ensures that the process improvement is realized.
For each phase of the lifecycle, following are the goals;
- Design Goals
- Capture executive vision
- Process nomination
- Process prioritization
- Process discovery
- Process analysis
- Modeling Goals
- Create a process model
- Process adjustments
Process simulation
- Execution Goals
- Implement the process model as a process application
- Adjust business process requirements as needed
- Deploy and monitor the process application
- Optimization Goals
- Analyze and evaluate process performance data
- Evaluate the business processability to meet new business goals
* After the business practices or external conditions change or the current process is no longer optimal, BPM iterates again through the lifecycle.
- This continual iteration allows the effective management of business processes.
- A true BPM implementation tool allows these iterations to be easily applied









